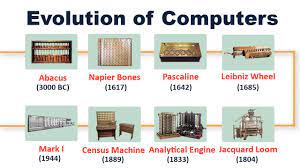
The Evolution of Computers: A Brief History
Computers have come a long way since their inception, evolving from room-sized machines with limited functionality to powerful devices that fit in the palm of our hands. Let’s take a journey through the history of computers to see how they have evolved over time.
First Generation Computers (1940s-1950s)
The first generation of computers emerged in the 1940s and 1950s. These early computers were massive in size, using vacuum tubes for processing data. They were primarily used for complex calculations and military applications.
Second Generation Computers (1950s-1960s)
The second generation of computers saw the introduction of transistors, which replaced vacuum tubes. This led to smaller and more reliable computers that were faster and more energy-efficient than their predecessors.
Third Generation Computers (1960s-1970s)
In the 1960s and 1970s, third-generation computers were developed, using integrated circuits that further reduced the size and cost of computers. This era saw the rise of mainframe computers and the development of time-sharing systems.
Fourth Generation Computers (1970s-Present)
The fourth generation of computers, starting in the 1970s, brought about microprocessors and personal computers. This revolutionized computing by making it accessible to individuals and businesses, leading to the digital age we live in today.
Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)
Currently, we are witnessing advancements in artificial intelligence, quantum computing, and other cutting-edge technologies that are shaping the future of computing. The fifth generation of computers promises even greater capabilities and possibilities than ever before.
In conclusion, the evolution of computers has been a remarkable journey marked by constant innovation and technological advancements. From bulky machines with limited processing power to sleek devices that can perform complex tasks with ease, computers have truly transformed our world in ways we could have never imagined.
From Abacus to AI: Tracing the Revolutionary Timeline of Computer History
- The history of computers dates back to ancient times with devices like the abacus.
- The first mechanical computer, Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine, was conceptualized in the 1830s.
- The invention of the electronic computer can be traced to the mid-20th century with machines like ENIAC.
- Transistors revolutionized computing in the 1950s by replacing bulky vacuum tubes in computers.
- The development of integrated circuits in the 1960s led to smaller and more powerful computers.
- Personal computers became popular in the 1980s with machines like the IBM PC and Apple Macintosh.
- The internet boom of the 1990s further transformed computing, connecting millions of users worldwide.
- Advancements in artificial intelligence and quantum computing are shaping the future of computer technology.
The history of computers dates back to ancient times with devices like the abacus.
The history of computers traces its roots back to ancient times, where rudimentary devices like the abacus were used for performing basic calculations. These early tools paved the way for the development of more sophisticated computing machines over the centuries, leading to the revolutionary advancements in technology that have shaped the modern world we live in today.
The first mechanical computer, Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine, was conceptualized in the 1830s.
The first mechanical computer, Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine, was conceptualized in the 1830s, marking a significant milestone in the history of computers. Designed to perform complex calculations through a series of gears and levers, the Analytical Engine laid the foundation for modern computing concepts. Although it was never fully built during Babbage’s lifetime, its innovative design and theoretical principles paved the way for future generations of computers and inspired further advancements in technology.
The invention of the electronic computer can be traced to the mid-20th century with machines like ENIAC.
The invention of the electronic computer can be traced back to the mid-20th century, with groundbreaking machines like ENIAC paving the way for modern computing. ENIAC, which stands for Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer, was one of the first electronic general-purpose computers and represented a significant leap forward in computational technology. Its development marked a pivotal moment in the history of computers, setting the stage for further innovations that would revolutionize the way we live and work today.
Transistors revolutionized computing in the 1950s by replacing bulky vacuum tubes in computers.
Transistors played a pivotal role in revolutionizing computing during the 1950s by replacing the bulky vacuum tubes that were previously used in computers. This technological advancement not only led to smaller and more reliable computers but also paved the way for faster processing speeds and increased energy efficiency. The introduction of transistors marked a significant milestone in the evolution of computers, setting the stage for further innovations that would ultimately shape the modern computing landscape.
The development of integrated circuits in the 1960s led to smaller and more powerful computers.
The development of integrated circuits in the 1960s marked a significant milestone in the history of computers. These tiny electronic components revolutionized the industry by enabling the creation of smaller, more powerful computers. Integrated circuits replaced the bulky and less efficient transistor-based systems, paving the way for advancements in computing technology that would ultimately lead to the widespread use of personal computers and other modern devices we rely on today.
Personal computers became popular in the 1980s with machines like the IBM PC and Apple Macintosh.
Personal computers became widely popular in the 1980s, thanks to groundbreaking machines such as the IBM PC and Apple Macintosh. These iconic devices revolutionized the way individuals interacted with technology, bringing computing power and functionality directly into people’s homes and offices. The user-friendly interfaces and innovative features of these personal computers paved the way for a new era of digital communication, creativity, and productivity. The 1980s marked a significant turning point in the history of computers, as personal computing became more accessible and integrated into everyday life.
The internet boom of the 1990s further transformed computing, connecting millions of users worldwide.
The internet boom of the 1990s marked a significant turning point in the history of computers, revolutionizing the way people interacted and accessed information. This era saw the rapid growth of the World Wide Web, connecting millions of users worldwide and enabling unprecedented communication and collaboration on a global scale. The emergence of e-commerce, social media, and online services during this time reshaped society and paved the way for a more interconnected and digital future.
Advancements in artificial intelligence and quantum computing are shaping the future of computer technology.
Advancements in artificial intelligence and quantum computing are playing a pivotal role in shaping the future of computer technology. Artificial intelligence is enabling computers to mimic human cognitive functions, leading to breakthroughs in areas such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision. On the other hand, quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to perform complex calculations at speeds unimaginable with classical computers. These cutting-edge technologies are paving the way for a new era of innovation and possibilities in the field of computer science, promising to revolutionize how we approach various challenges and opportunities in the digital age.
