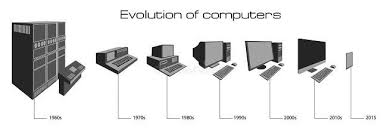
The Evolution of Computer Generation
Computers have come a long way since their inception, evolving through distinct generations that have shaped the technology we use today.
First Generation (1940s-1950s)
The first generation of computers used vacuum tubes for processing and magnetic drums for memory. These computers were large, expensive, and consumed a lot of power.
Second Generation (1950s-1960s)
The second generation saw the introduction of transistors, which made computers smaller, faster, and more reliable. Magnetic core memory was also developed during this time.
Third Generation (1960s-1970s)
The third generation brought about the use of integrated circuits, which further reduced the size and cost of computers. Operating systems and high-level programming languages were also developed.
Fourth Generation (1970s-1980s)
The fourth generation saw the rise of microprocessors, enabling personal computers to become more affordable and accessible to the general public. GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces) were also introduced.
Fifth Generation (1980s-Present)
The fifth generation is characterized by advancements in artificial intelligence, parallel processing, and networking technologies. This era has seen the rise of smartphones, tablets, and cloud computing.
As we look towards the future, it’s clear that the evolution of computer generation will continue to shape our world in ways we can’t yet imagine.
Key Benefits of Computer Evolution Across Generations
- Increased processing speed and efficiency with each generation.
- Reduction in size and cost of computers, making them more accessible to a wider audience.
- Development of new technologies such as integrated circuits and microprocessors.
- Introduction of user-friendly interfaces like GUIs, improving usability for non-technical users.
- Advancements in storage capacity and memory capabilities.
- Innovation in networking technologies, enabling global connectivity.
Challenges Posed by the Evolution of Computer Generations
- Obsolete technology and hardware become difficult to maintain and repair.
- Rapid advancements can lead to a short lifespan for newer technologies, making investments quickly outdated.
- Increased complexity of systems may require specialized knowledge and training to operate effectively.
- Environmental concerns arise due to the disposal of outdated electronic components and e-waste.
- Privacy and security risks escalate with the interconnected nature of modern computing systems.
- Growing digital divide as access to newer technologies becomes limited for certain populations.
Increased processing speed and efficiency with each generation.
With each evolution of computer generation, we have witnessed a remarkable increase in processing speed and efficiency. From the early days of vacuum tube computers to the modern era of powerful microprocessors, advancements in technology have enabled computers to perform tasks faster and more efficiently than ever before. This increased processing speed and efficiency have revolutionized industries, improved productivity, and opened up new possibilities for innovation and creativity in the digital age.
Reduction in size and cost of computers, making them more accessible to a wider audience.
One significant advantage of the evolution of computer generation is the reduction in size and cost of computers, making them more accessible to a wider audience. As technology has advanced through different generations, computers have become smaller, more powerful, and more affordable. This has democratized access to computing devices, allowing individuals from various backgrounds and income levels to own and benefit from the use of computers. The increased accessibility has opened up new opportunities for education, communication, innovation, and overall societal progress.
Development of new technologies such as integrated circuits and microprocessors.
The evolution of computer generation has brought about significant advancements in technology, such as the development of integrated circuits and microprocessors. These innovations have revolutionized the computing industry by making computers smaller, faster, and more powerful. Integrated circuits allowed for the creation of complex electronic circuits on a single chip, while microprocessors enabled the development of affordable personal computers that could perform a wide range of tasks. These technologies have paved the way for the digital age we live in today, driving progress and innovation across various industries.
Introduction of user-friendly interfaces like GUIs, improving usability for non-technical users.
The introduction of user-friendly interfaces like Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) has been a significant pro in the evolution of computer generation, greatly improving usability for non-technical users. GUIs provide intuitive visual representations that make it easier for individuals to interact with computers without needing to have a deep understanding of technical concepts. This advancement has democratized access to technology, empowering a wider range of users to harness the power of computers for various tasks and activities, ultimately enhancing efficiency and productivity in both personal and professional settings.
Advancements in storage capacity and memory capabilities.
One significant pro of the evolution of computer generation is the remarkable advancements in storage capacity and memory capabilities. Over the years, we have witnessed a tremendous increase in the amount of data that computers can store and process efficiently. From bulky magnetic drums to compact solid-state drives, the evolution of storage technology has enabled us to store vast amounts of information in smaller and more reliable formats. Similarly, improvements in memory capabilities have allowed for faster data access and seamless multitasking, enhancing overall computing performance and user experience. These advancements have revolutionized how we store, retrieve, and manipulate data, empowering us to handle complex tasks with unprecedented speed and efficiency.
Innovation in networking technologies, enabling global connectivity.
One of the significant benefits of the evolution of computer generation is the innovation in networking technologies, which has revolutionized global connectivity. With advancements such as high-speed internet, wireless communication, and cloud computing, people around the world can now easily connect and communicate with each other in real-time. This interconnectedness has transformed how we work, socialize, and access information, breaking down geographical barriers and fostering collaboration on a global scale. The continuous development of networking technologies has paved the way for a more interconnected world where ideas, cultures, and knowledge can be shared instantaneously across borders.
Obsolete technology and hardware become difficult to maintain and repair.
As the evolution of computer generation progresses, one significant challenge that arises is the issue of obsolete technology and hardware becoming increasingly difficult to maintain and repair. With each new generation of computers introducing faster, more advanced components, older technology quickly becomes outdated and unsupported. This can lead to difficulties in finding replacement parts, accessing technical support, and obtaining compatible software for older systems. As a result, users may face obstacles in keeping their outdated hardware operational, ultimately leading to increased costs and potential disruptions in their computing experience.
Rapid advancements can lead to a short lifespan for newer technologies, making investments quickly outdated.
One significant drawback of the rapid evolution of computer generation is the short lifespan that newer technologies often face. As advancements occur at a breakneck pace, investments in cutting-edge technologies can quickly become outdated, requiring constant upgrades and replacements to keep up with the latest developments. This cycle of obsolescence can be costly for individuals and organizations alike, as they struggle to stay current in an ever-changing technological landscape.
Increased complexity of systems may require specialized knowledge and training to operate effectively.
As computer technology evolves, one significant con is the increased complexity of systems that may demand specialized knowledge and training to operate effectively. With advancements in hardware, software, and networking technologies, users may find it challenging to keep up with the intricate workings of modern computer systems. This can lead to a barrier for individuals who lack the necessary expertise, potentially limiting their ability to fully utilize and benefit from the latest technological innovations. As systems become more sophisticated, the need for specialized training and education in operating and troubleshooting these complex systems becomes essential to navigate the digital landscape effectively.
Environmental concerns arise due to the disposal of outdated electronic components and e-waste.
One significant con of the evolution of computer generation is the environmental impact caused by the disposal of outdated electronic components and e-waste. As technology advances rapidly, older devices become obsolete at a quicker pace, leading to a surge in electronic waste that poses serious environmental challenges. Improper disposal of e-waste can result in harmful chemicals leaching into soil and water sources, contributing to pollution and potential health risks for both humans and wildlife. Addressing these environmental concerns requires sustainable practices in electronic recycling and responsible disposal methods to minimize the negative impact on our planet.
Privacy and security risks escalate with the interconnected nature of modern computing systems.
Privacy and security risks have escalated with the interconnected nature of modern computing systems. As computers have evolved through generations, becoming more interconnected and reliant on networks, the potential for data breaches, cyber attacks, and privacy invasions has increased significantly. The vast amount of personal information stored online and shared between devices poses a significant threat to individual privacy and security. As technology continues to advance, it is crucial for individuals and organizations to prioritize cybersecurity measures to mitigate these risks and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or exploitation.
Growing digital divide as access to newer technologies becomes limited for certain populations.
As the evolution of computer generation progresses, a concerning con that emerges is the growing digital divide, where access to newer technologies becomes limited for certain populations. This disparity in access can further exacerbate existing inequalities, hindering individuals and communities from fully participating in the digital age. Without equitable access to the latest technologies, marginalized groups may face barriers in education, employment opportunities, and overall societal advancement. Addressing this issue is crucial to ensure that everyone has the chance to benefit from the advancements in computer technology and bridge the digital divide for a more inclusive future.
