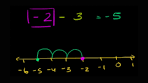
The Importance of Learning Integers with Khan Academy
Integers are a fundamental concept in mathematics, and understanding them is crucial for building a strong foundation in math. Khan Academy offers a comprehensive and interactive platform for learning about integers that can benefit students of all levels.
Through Khan Academy’s intuitive lessons and exercises, students can grasp the concept of integers, including positive and negative numbers, absolute value, addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The platform provides step-by-step explanations and practice problems to help reinforce learning and improve mathematical skills.
One of the key advantages of using Khan Academy for learning integers is the ability to learn at your own pace. Students can progress through the material at a speed that suits their individual learning style, allowing for a customized learning experience that promotes understanding and retention.
Additionally, Khan Academy offers a variety of resources such as videos, articles, and interactive tools that cater to different learning preferences. Whether you are a visual learner who benefits from watching instructional videos or prefer hands-on practice with interactive exercises, Khan Academy has something for everyone.
By mastering integers through Khan Academy, students can develop critical thinking skills, improve problem-solving abilities, and build a solid mathematical foundation that will serve them well in future studies. Whether you are a student looking to enhance your math skills or an educator seeking additional resources for teaching integers, Khan Academy provides a valuable educational platform that can support your academic goals.
Start exploring Khan Academy’s integers lessons today and unlock the potential for mathematical growth and understanding!
Mastering Integers: 9 Essential Tips for Success with Khan Academy
- Integers are whole numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero.
- On a number line, integers to the right are greater than those on the left.
- Adding a positive integer to another positive integer results in a larger sum.
- Subtracting a negative integer is equivalent to adding its absolute value.
- Multiplying or dividing two integers with the same signs results in a positive number.
- Multiplying or dividing two integers with different signs results in a negative number.
- The order of operations (PEMDAS) applies when working with integers and other mathematical operations.
- Integer problems often involve concepts like absolute value and comparing magnitudes.
- Practice regularly to improve your understanding and proficiency with integer operations.
Integers are whole numbers that can be positive, negative, or zero.
Integers encompass whole numbers that include positive values, negative values, and zero. Understanding the concept of integers is essential in mathematics as they form the basis for a wide range of calculations and problem-solving scenarios. By grasping the nature of integers as numbers that can be either positive, negative, or zero, students can navigate mathematical operations with confidence and precision, laying a solid foundation for more advanced math concepts.
On a number line, integers to the right are greater than those on the left.
Understanding the concept that on a number line, integers to the right are greater than those on the left is fundamental in grasping the relative values of integers. This visual representation helps students visualize the order of integers and comprehend their relationships in a clear and intuitive manner. By internalizing this tip from Khan Academy, learners can enhance their understanding of number line concepts and develop a solid foundation for working with integers in various mathematical contexts.
Adding a positive integer to another positive integer results in a larger sum.
When adding a positive integer to another positive integer in mathematics, the result is always a larger sum. This fundamental concept is essential to understanding the behavior of positive integers and reinforces the idea that combining two positive quantities leads to a greater total value. By grasping this principle through Khan Academy’s intuitive lessons on integers, students can enhance their mathematical skills and develop a solid foundation for more advanced concepts in arithmetic and beyond.
Subtracting a negative integer is equivalent to adding its absolute value.
When learning about integers on Khan Academy, a valuable tip to remember is that subtracting a negative integer is equivalent to adding its absolute value. This concept simplifies the process of subtracting negative numbers and helps students understand the relationship between positive and negative integers. By applying this rule, learners can confidently perform subtraction operations involving negative numbers with ease and accuracy, enhancing their overall grasp of integer arithmetic.
Multiplying or dividing two integers with the same signs results in a positive number.
When multiplying or dividing two integers with the same signs, the result will always be a positive number. This fundamental rule in mathematics is crucial to understanding the relationship between integers and their operations. By grasping this concept on Khan Academy’s platform, students can strengthen their knowledge of integers and enhance their problem-solving skills. Understanding the outcome of multiplying or dividing integers with the same signs as positive reinforces the foundational principles of mathematics and lays a solid groundwork for more complex mathematical concepts.
Multiplying or dividing two integers with different signs results in a negative number.
When multiplying or dividing two integers with different signs, the result will always be a negative number. This fundamental rule in integer arithmetic is essential to understand, as it demonstrates the relationship between positive and negative numbers. By grasping this concept on Khan Academy’s platform, students can deepen their comprehension of integers and strengthen their mathematical skills.
The order of operations (PEMDAS) applies when working with integers and other mathematical operations.
Understanding the order of operations, commonly remembered by the acronym PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division from left to right, Addition and Subtraction from left to right), is essential when working with integers and other mathematical operations. By following the correct order of operations, students can ensure that they solve mathematical expressions accurately and avoid errors. Khan Academy provides clear explanations and practice exercises on using PEMDAS with integers, helping learners master this fundamental concept in mathematics.
Integer problems often involve concepts like absolute value and comparing magnitudes.
When tackling integer problems on Khan Academy, it is important to remember that these problems frequently incorporate concepts such as absolute value and comparing magnitudes. Understanding how to work with absolute values and compare the magnitudes of integers is key to solving a wide range of integer-related problems effectively. By mastering these fundamental concepts on Khan Academy, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and build a strong foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Practice regularly to improve your understanding and proficiency with integer operations.
Regular practice is key to enhancing your understanding and proficiency with integer operations on Khan Academy. By consistently engaging with exercises and problems related to integers, you can solidify your knowledge and sharpen your skills. The more you practice, the more comfortable and confident you will become in handling integer operations, leading to improved mastery of this fundamental mathematical concept. Make practicing regularly a priority on Khan Academy to see significant progress in your understanding of integers.
