The Evolution of Computers: A Journey Through History
Computers have become an integral part of our lives, revolutionizing the way we work, communicate, and access information. But have you ever wondered how these incredible machines came to be? Let’s take a journey through the fascinating history of computers and explore their evolution.
The Birth of Computing
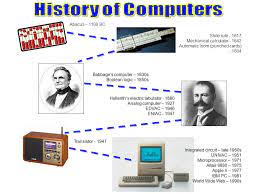
The origins of computers can be traced back to ancient times when humans developed tools to aid in calculations. The abacus, invented around 2400 BCE, was one such early device used for arithmetic calculations. Fast forward to the 17th century, and we encounter the mechanical calculator invented by Blaise Pascal, which could perform basic arithmetic operations.
The Advent of Programmable Machines
In the early 19th century, inventors like Charles Babbage envisioned machines that could perform complex calculations automatically. Babbage’s Analytical Engine, designed in the 1830s, is considered a precursor to modern computers. It featured mechanical components and could be programmed using punched cards.
However, it wasn’t until the mid-20th century that electronic computers emerged. The Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC), developed during World War II in the United States, was one of the earliest electronic general-purpose computers. It utilized vacuum tubes for processing data and was massive in size.
The Rise of Transistors and Microprocessors
In the late 1940s, transistors were invented by researchers at Bell Labs. These tiny electronic components replaced bulky vacuum tubes and offered improved reliability and efficiency. The invention of transistors paved the way for smaller and more powerful computers.
In 1971, Intel introduced the first microprocessor – the Intel 4004. This single-chip CPU revolutionized the computer industry by integrating the central processing unit onto a small piece of silicon. Microprocessors enabled the development of personal computers, bringing computing power to individuals and businesses.
The Era of Personal Computers
In the late 1970s and early 1980s, companies like Apple and IBM introduced personal computers that were affordable and user-friendly. These machines featured graphical user interfaces (GUIs) and brought computing to the masses. The release of the IBM PC in 1981 further accelerated the adoption of personal computers.
The Internet Age
In the 1990s, the internet revolutionized computing by connecting computers worldwide. Tim Berners-Lee’s invention of the World Wide Web in 1989 made it easier to access information and communicate globally. The internet opened up new possibilities for e-commerce, social networking, and online collaboration.
Advancements in Computing Today
Today, we witness rapid advancements in computing technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, virtual reality, and quantum computing. These innovations continue to push the boundaries of what computers can do and shape our future.
From humble beginnings with mechanical calculators to powerful supercomputers and portable devices we carry in our pockets, computers have come a long way. They have transformed every aspect of our lives and continue to evolve at an astonishing pace.
As we look back on this incredible journey through computer history, we can only wonder what exciting developments lie ahead as technology continues to advance.
From Analytical Engines to the Internet Age: 8 Milestones in Computer History
- The history of computers dates back to the 1800s when mechanical devices like Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine were conceptualized.
- The first electronic computer, ENIAC, was developed in the 1940s and used vacuum tubes for calculations.
- Transistors replaced vacuum tubes in the 1950s, making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable.
- In the 1960s, integrated circuits were invented, leading to further miniaturization and increased computing power.
- The development of microprocessors in the early 1970s revolutionized computing by integrating multiple components on a single chip.
- Personal computers became popular in the late 1970s with machines like Apple II and Commodore PET entering homes and offices.
- The invention of graphical user interfaces (GUI) in the early 1980s made computers more user-friendly and accessible to non-experts.
- The internet revolutionized computing in the late 20th century, connecting millions of computers worldwide and enabling global communication.
The history of computers dates back to the 1800s when mechanical devices like Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine were conceptualized.
The history of computers stretches back to the 1800s, where visionary thinkers like Charles Babbage conceptualized mechanical devices such as the Analytical Engine. These early inventions laid the groundwork for the development of modern computers, showcasing the human desire to automate complex calculations and tasks. Babbage’s visionary ideas paved the way for subsequent advancements in computing technology, leading us on a remarkable journey through time to the powerful and sophisticated machines we have today.
The first electronic computer, ENIAC, was developed in the 1940s and used vacuum tubes for calculations.
In the 1940s, a significant milestone in the history of computers was achieved with the development of the Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer (ENIAC). This groundbreaking machine marked the advent of electronic computing. ENIAC utilized vacuum tubes, which were large, fragile, and consumed a significant amount of power. Despite these limitations, ENIAC paved the way for future advancements in computing technology and laid the foundation for the modern digital age we live in today.
Transistors replaced vacuum tubes in the 1950s, making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable.
In the 1950s, a significant breakthrough occurred in the history of computers with the introduction of transistors, which replaced the bulky and less efficient vacuum tubes. This technological advancement revolutionized the field by making computers smaller, faster, and more reliable. Transistors, being smaller in size and consuming less power, allowed for the development of compact electronic devices that could perform complex calculations with greater efficiency. This milestone paved the way for further advancements in computer technology and set the stage for the miniaturization and portability of computers in subsequent years.
In the 1960s, integrated circuits were invented, leading to further miniaturization and increased computing power.
During the 1960s, a significant breakthrough in computer technology occurred with the invention of integrated circuits. These tiny electronic components revolutionized the field by enabling further miniaturization and significantly increasing computing power. Integrated circuits, also known as microchips, allowed for the integration of multiple transistors and other electronic components onto a single silicon chip. This advancement paved the way for smaller, more efficient, and more powerful computers, setting the stage for the rapid advancement of technology that we continue to witness today.
The development of microprocessors in the early 1970s revolutionized computing by integrating multiple components on a single chip.
The development of microprocessors in the early 1970s marked a significant turning point in the history of computers. These tiny chips revolutionized computing by integrating multiple components onto a single piece of silicon. Prior to microprocessors, computers relied on numerous separate components that occupied large physical spaces and required complex wiring. The introduction of microprocessors not only drastically reduced the size and complexity of computers but also increased their processing power and efficiency. This breakthrough paved the way for the development of personal computers, making computing accessible to individuals and businesses alike. The integration of multiple components on a single chip was a game-changer, propelling the evolution of computers into new realms of possibility.
Personal computers became popular in the late 1970s with machines like Apple II and Commodore PET entering homes and offices.
In the late 1970s, personal computers experienced a surge in popularity as machines like the Apple II and Commodore PET made their way into homes and offices. These user-friendly and affordable computers revolutionized the way people interacted with technology. The Apple II, introduced in 1977, featured a graphical user interface and became a symbol of the emerging personal computer industry. Similarly, the Commodore PET, released in 1977 as well, offered a complete package with built-in keyboard and monitor. These early personal computers marked a significant milestone in computer history, bringing computing power directly to individuals and businesses, laying the foundation for the digital age we live in today.
The invention of graphical user interfaces (GUI) in the early 1980s made computers more user-friendly and accessible to non-experts.
The invention of graphical user interfaces (GUI) in the early 1980s marked a significant milestone in the history of computers. Prior to GUIs, computers primarily relied on text-based interfaces that were complex and intimidating for non-experts. However, with the introduction of GUIs, computers became more user-friendly and accessible to a wider audience. GUIs utilized icons, windows, and menus, allowing users to interact with computers through visual representations rather than relying solely on command-line inputs. This breakthrough in interface design revolutionized the way people interacted with computers, making them more intuitive and paving the way for widespread adoption by non-experts. Today, GUIs are an integral part of modern computing, enabling users around the world to navigate and utilize technology with ease.
The internet revolutionized computing in the late 20th century, connecting millions of computers worldwide and enabling global communication.
The internet revolutionized computing in the late 20th century, connecting millions of computers worldwide and enabling global communication. With the invention of the World Wide Web and the widespread adoption of internet technologies, people could easily access information, communicate with others across the globe, and engage in e-commerce. The internet opened up a whole new world of possibilities, transforming how we work, learn, socialize, and conduct business. It has become an integral part of our daily lives, connecting us in ways that were unimaginable just a few decades ago. The impact of the internet on computing is undeniable and continues to shape our modern digital landscape.
